

However, with good judgment and proper training and planning, it is possible to safely operate an aircraft in flat light conditions.As a result of this reflected light, it can give pilots the illusion that they are ascending or descending when they may actually be flying level.Flat light can completely obscure features of the terrain, creating an inability to distinguish distances and closure rates.Such conditions can occur anywhere in the world, primarily in snow covered areas but can occur in dust, sand, mud flats, or on glassy water.Flat light conditions are usually accompanied by overcast skies inhibiting any visual clues.It is not as severe as "white out" but the condition causes pilots to lose their depth-of-field and contrast in vision.Flat light is an optical illusion, also known as "sector or partial white out".The geological theory explaining continental drift is pl… Heat Transfer, Heat transfer is the energy flow that occurs between bodies as a result of a temperature difference.Flying in Flat Light, Brown Out Conditions, and White Out Conditions: It is the manner in which that heat is distributed throughout th… Continental Drift, IntroductionĬontinental drift is the slow movement of continents over the surface of Earth. It is also a term that describes process… Weather, Weather is the state of the atmosphere at any given time and place, determined by such factors as temperature, precipitation, cloud cover, humidity,… Atmospheric Circulation, IntroductionĪtmospheric circulation includes the movement of air on a global scale. See also Adiabatic heating Atmospheric circulation Atmospheric composition and structure Atmospheric inversion layers Atmospheric lapse rate Atmospheric pressure Convection (updrafts and downdrafts) Insolation and total solar irradiation Wind chill Wind shearĬonvection is the name for a means of heat transfer, as distinguished from conduction and radiation.

The advection fog forms as warm and moist air moves horizontally along the cooler surface and the air near the surface is cooled to its dew point. Advection fog usually occurs when the atmosphere is very stable so that moist (humid) air near the surface does not mix vertically with an overlying layer of drier air. Both processes contribute approximately equally because wind currents are much faster (higher rate) than ocean currents but ocean currents move substantially denser masses of molecules.Īdvection is also responsible for the formation of advection fog. The magnitude of heat transference depends on heat flux (the rate of heat transport), and flux in turn relates the transfer of heat energy in terms of area and time. Just as ocean currents permit heat transfer from areas of warm water to an area of water with cooler temperatures, advective winds allow the transfer of both sensible heat and latent heat (a function of humidity ).Īlthough advection processes are important heat equilibration mechanisms for both the atmosphere and the oceans, the speed and volume of mass transported differs greatly between the atmosphere and oceans. In contrast, vertical transfer occurs via conduction, convection, and radiation. In the atmosphere, advection is the sole process of lateral transfer of mass. For example, advection also takes place in the oceans where advection is broadened to include the lateral (horizontal) transfer of not only fluid mass and heat, but of other properties such and oxygen content and salinity. This is an important consideration when considering advection, because advection is usually more pronounced in the movement of fluids. Accordingly, winds are a result of advection, while air currents are a result of convection.Īlthough in a gaseous state, the atmosphere observes fluid-like dynamics. In contrast, convection, the vertical movement of mass or transfer of heat, manifests itself as air currents. Advective winds move from areas of higher temperature toward areas of lower temperature.
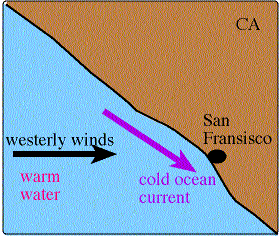
Currently, geologists debate the presence and role of substantial advective processes in Earth's mantle.ĭifferential pressures and temperatures drive the mass movement of air seeking equilibrium (the lowest energy state). Advection also takes place in the ocean in the form of currents. Accordingly, winds that blow across Earth's surface represent advectional movements of air. Advection is a lateral or horizontal transfer of mass, heat, or other property. Earth's atmosphere is a dynamic sea of gases in constant motion and Earth's oceans contain currents that move water across the globe.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
